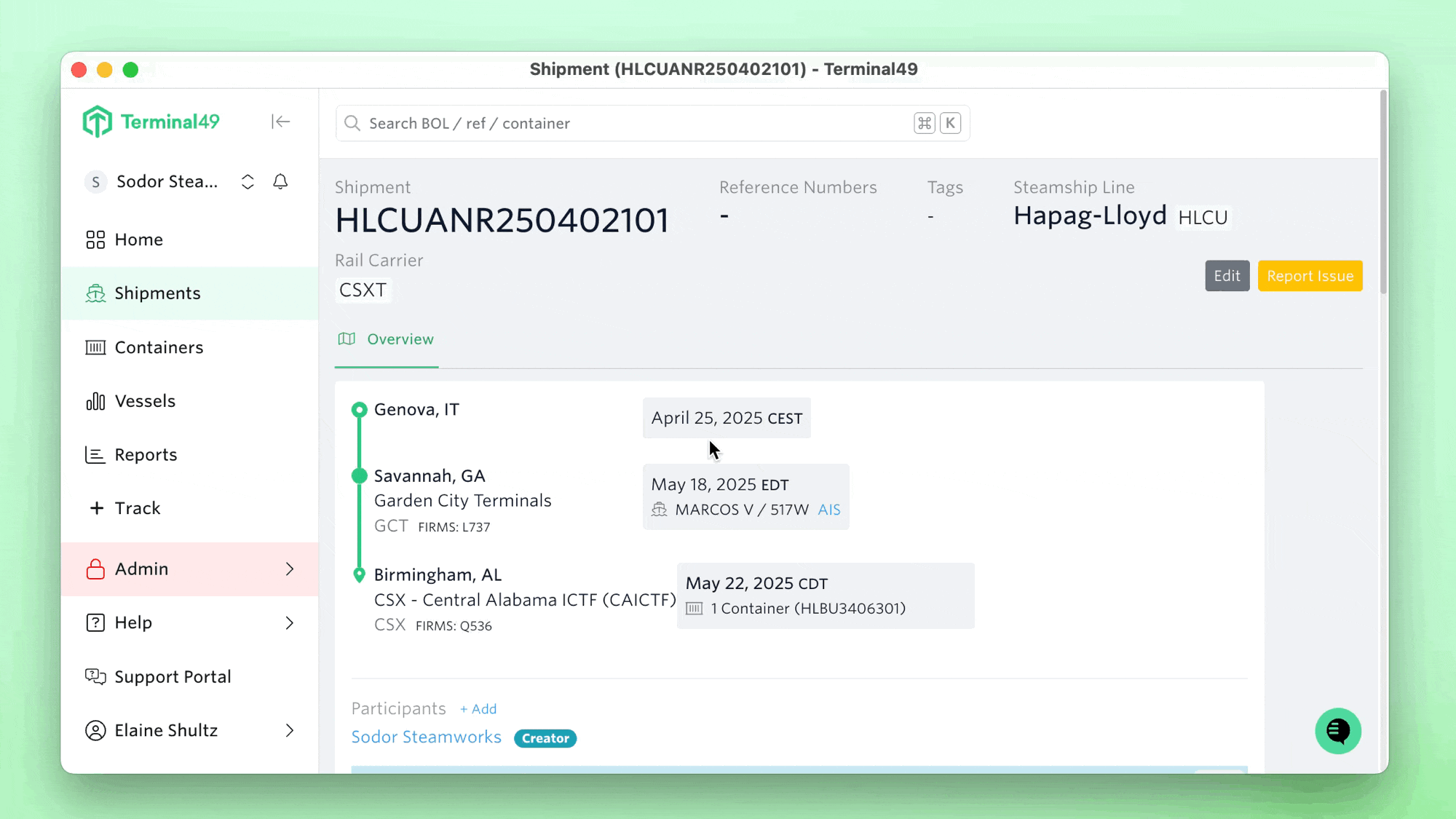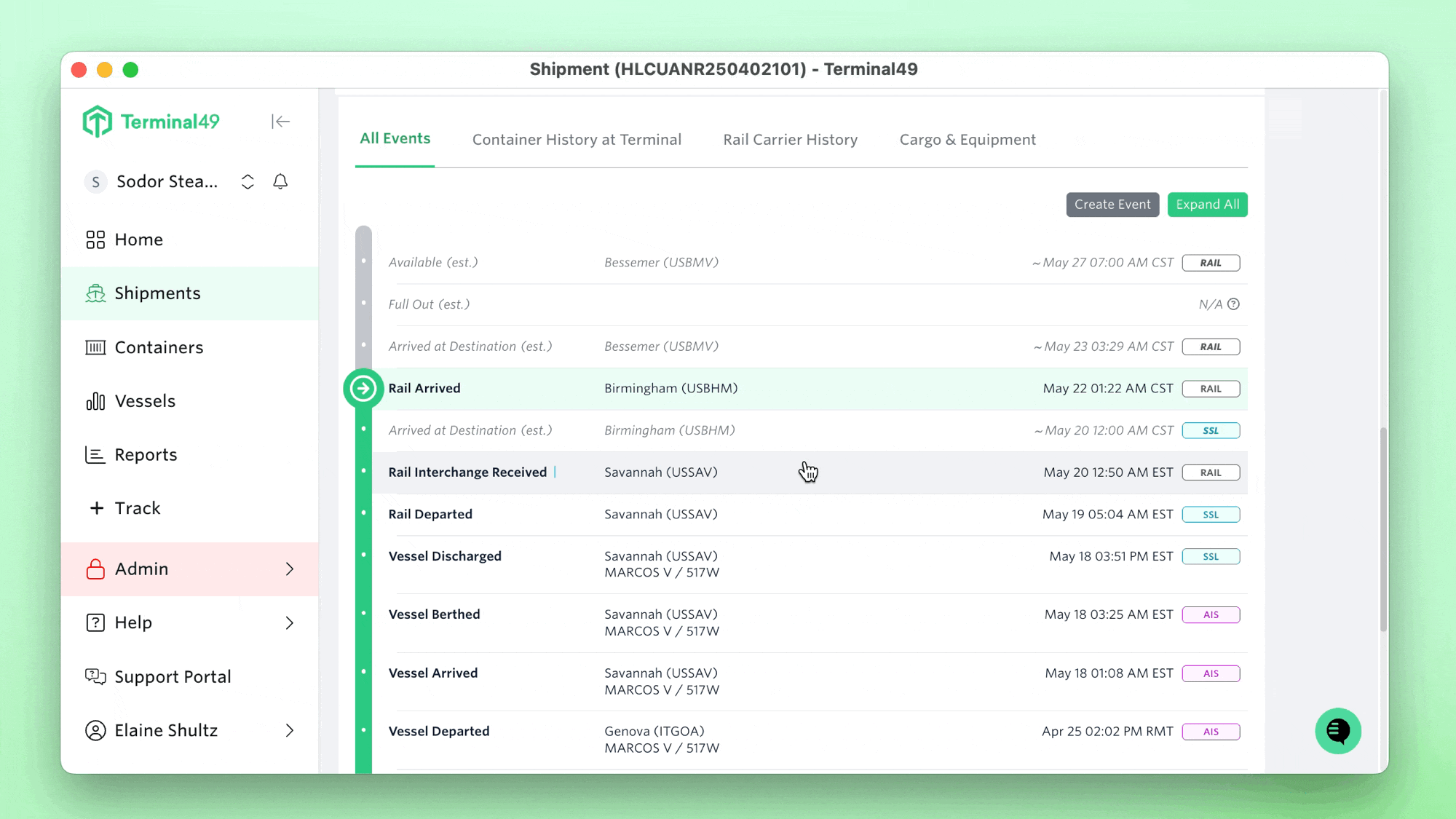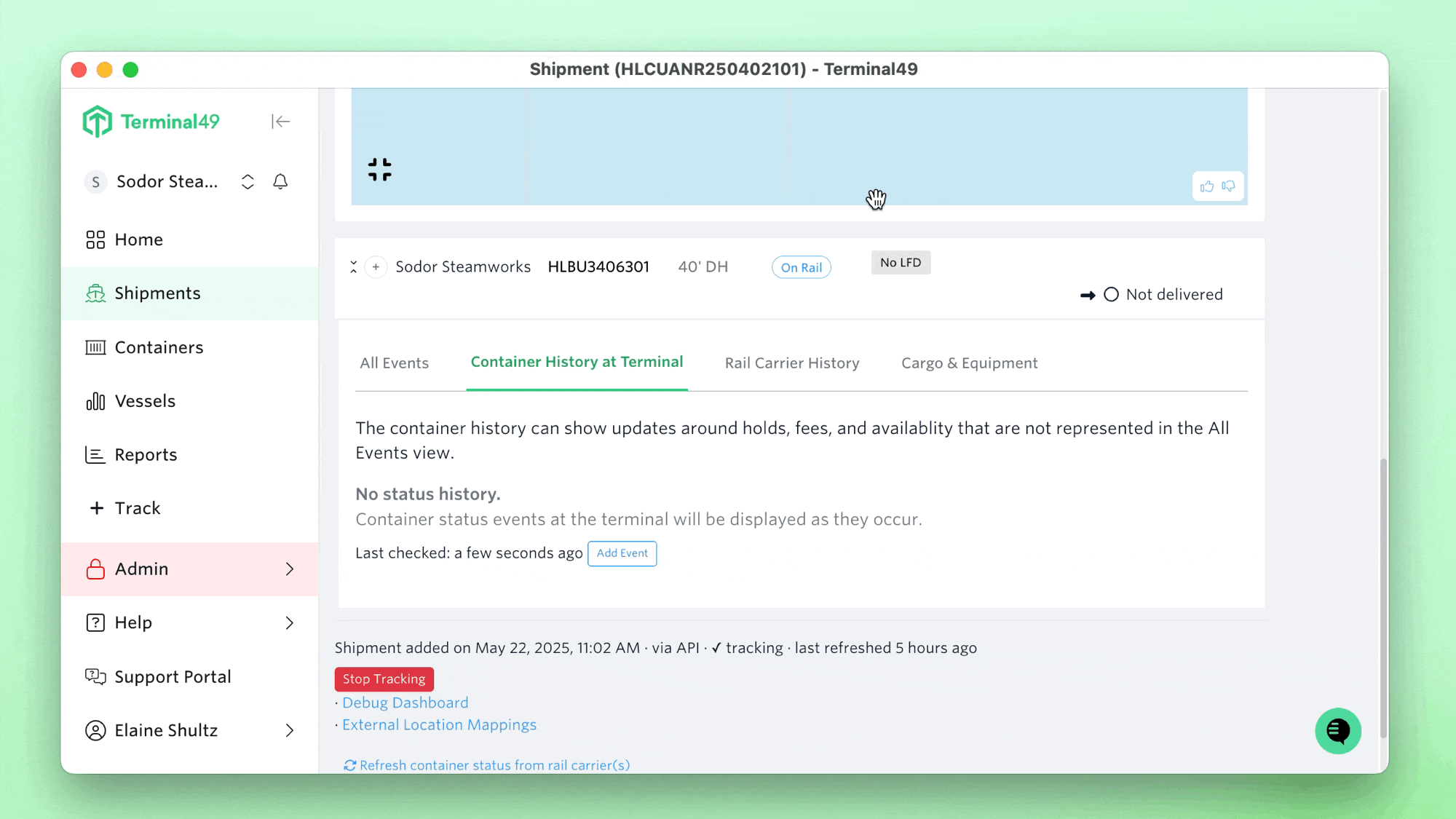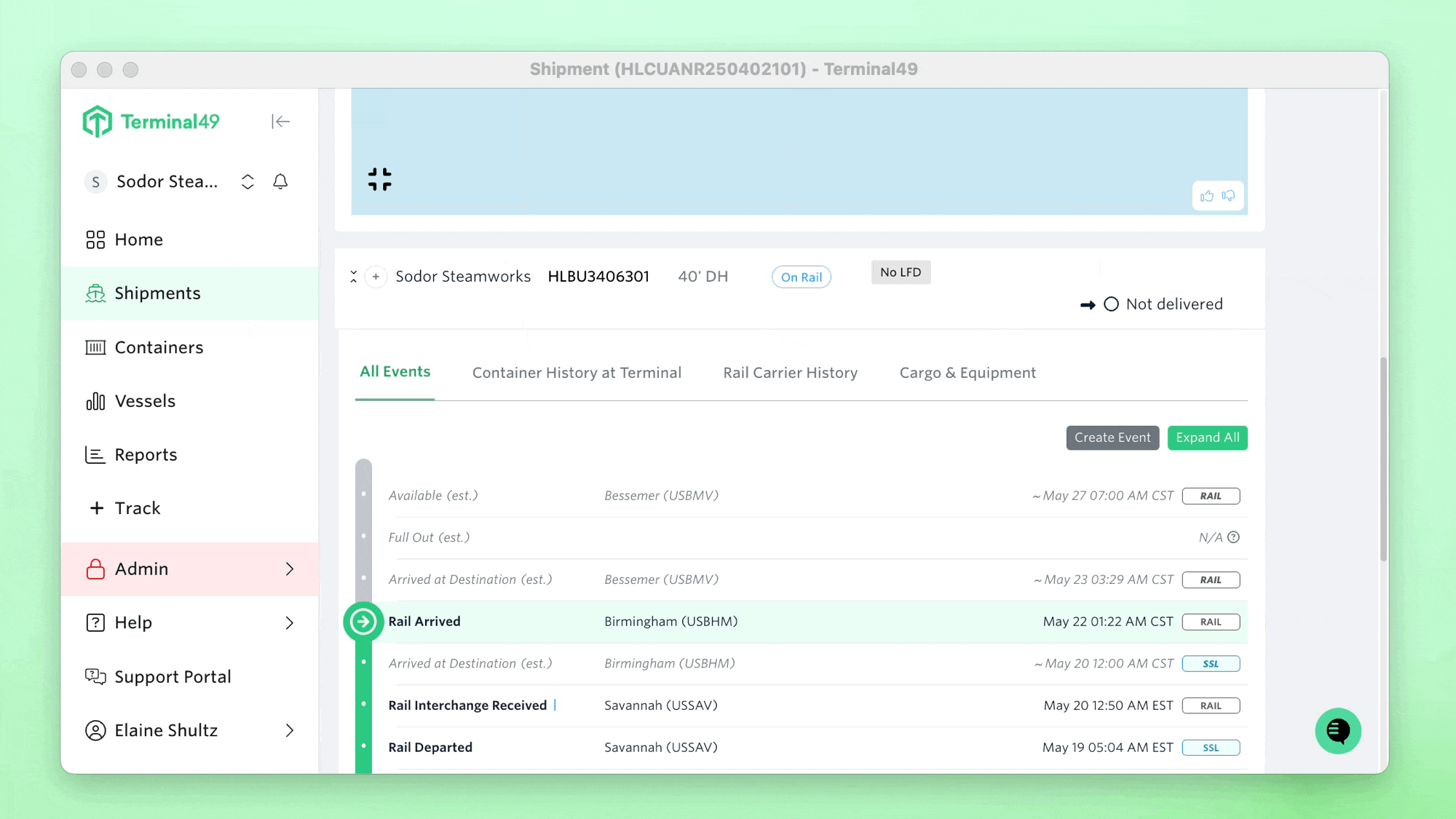
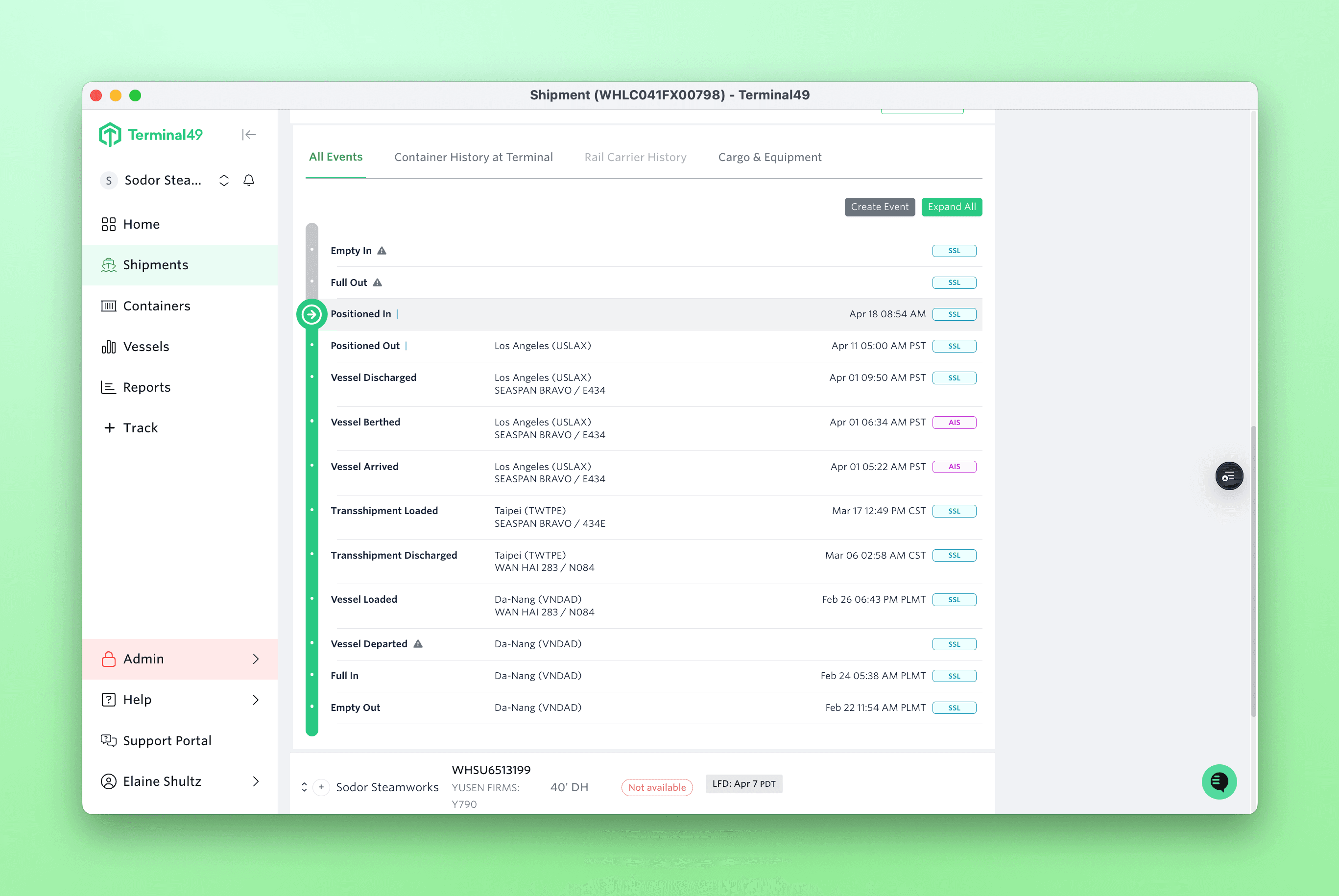
Supply chain disruptions are a dime a dozen. In shipping operations, a few disruptive forces can completely upend supply chains, as was seen with the 3-day ILA labor strike involving all major ports from Maine to Texas. While the strike was shorter than what many expected, it still has massive repercussions, with ripple effects expected to last for up to a month.
A tentative agreement until Jan. 15, 2025, is now in place after the Biden administration worked with USMX and ILA to hammer out a temporary deal. Whether the parties could come to an agreement at this moment, the consequences of it remains to be seen. A failure to ratify a deal by Jan. 15 could open the pandora’s box again, as the East and Gulf Coast ports are responsible for handling 55% of containers moving to and from the United States.
Scope of The ILA Strike That ‘Could-Have-Been’
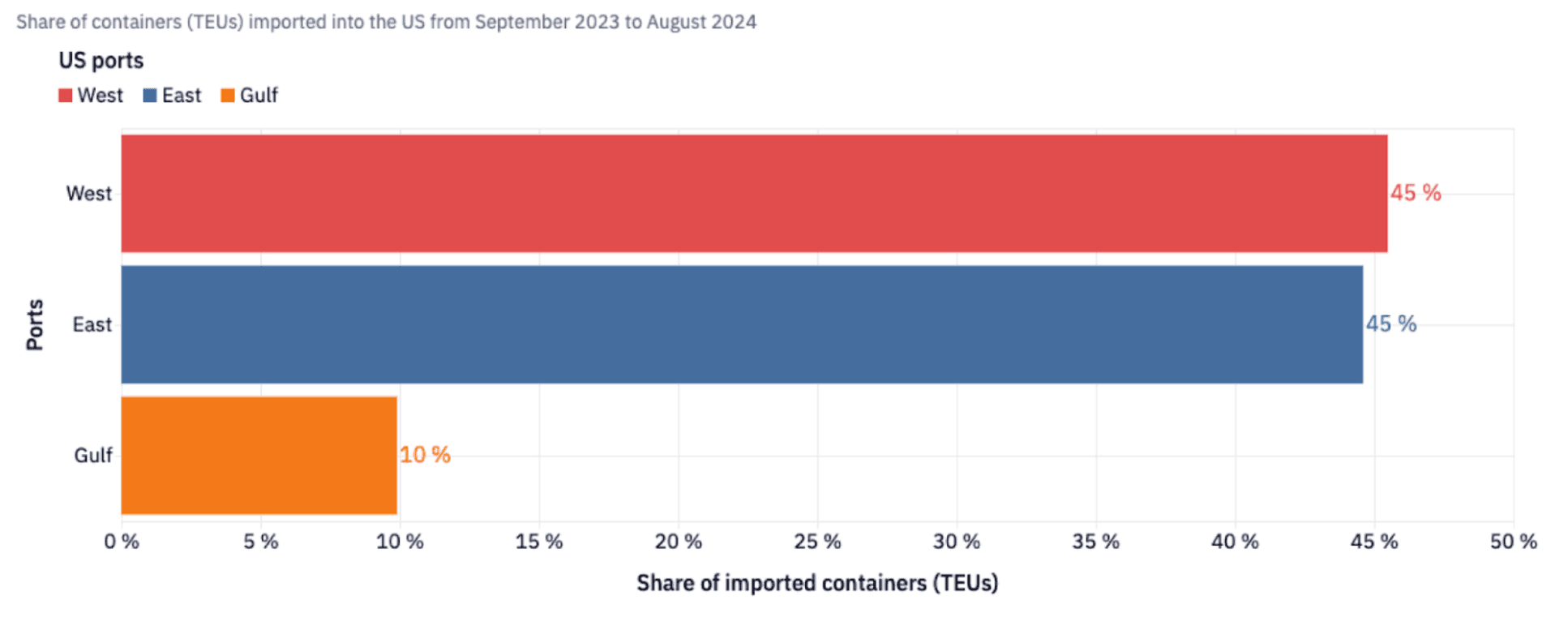
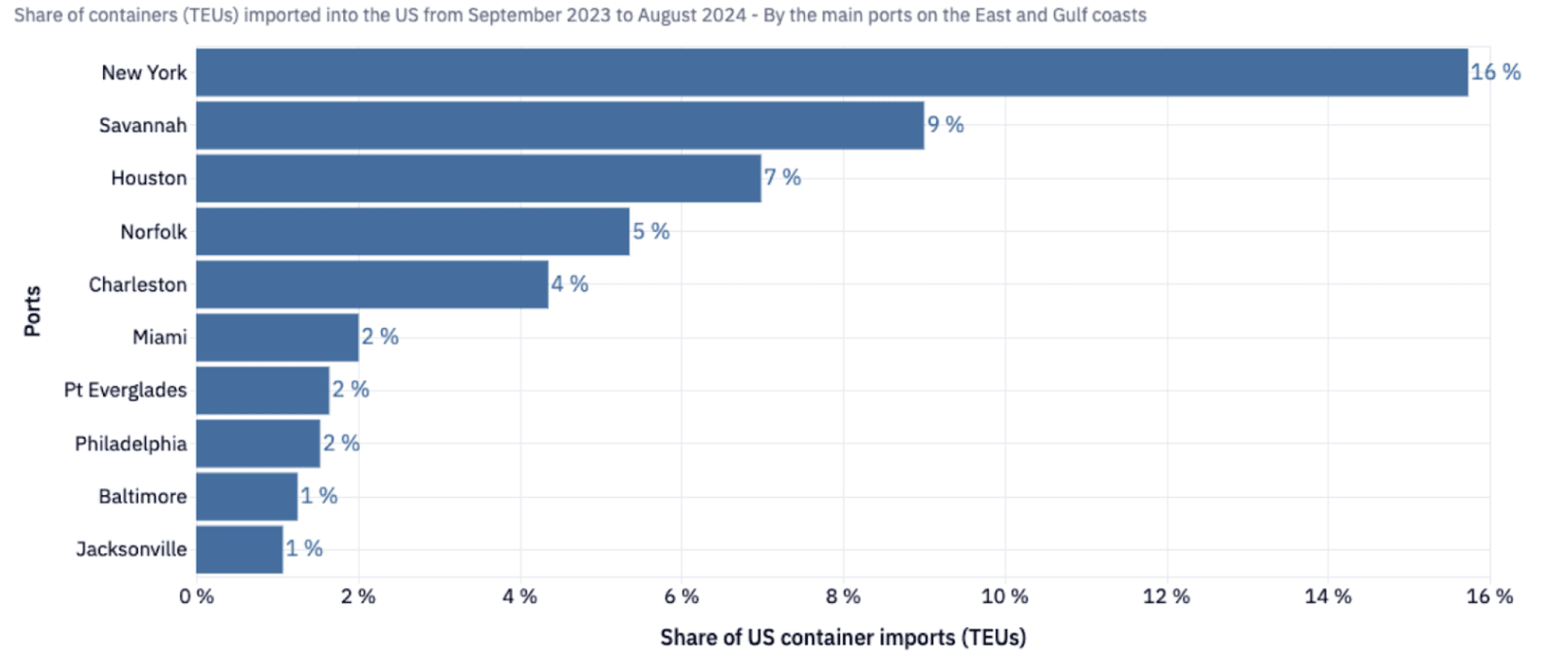
The 3-day ILA strike impacted ports operating throughout the East and Gulf Coasts, including key U.S. ports such as New York, Savannah, Houston, Norfolk, and Charleston, among others. These ports handle significant volumes of both domestic and international trade. And because they are critical gateways for goods entering or leaving the country, experts believe that the bottlenecks and delayed shipments resulting from the strike could cost the economy $5 billion daily.
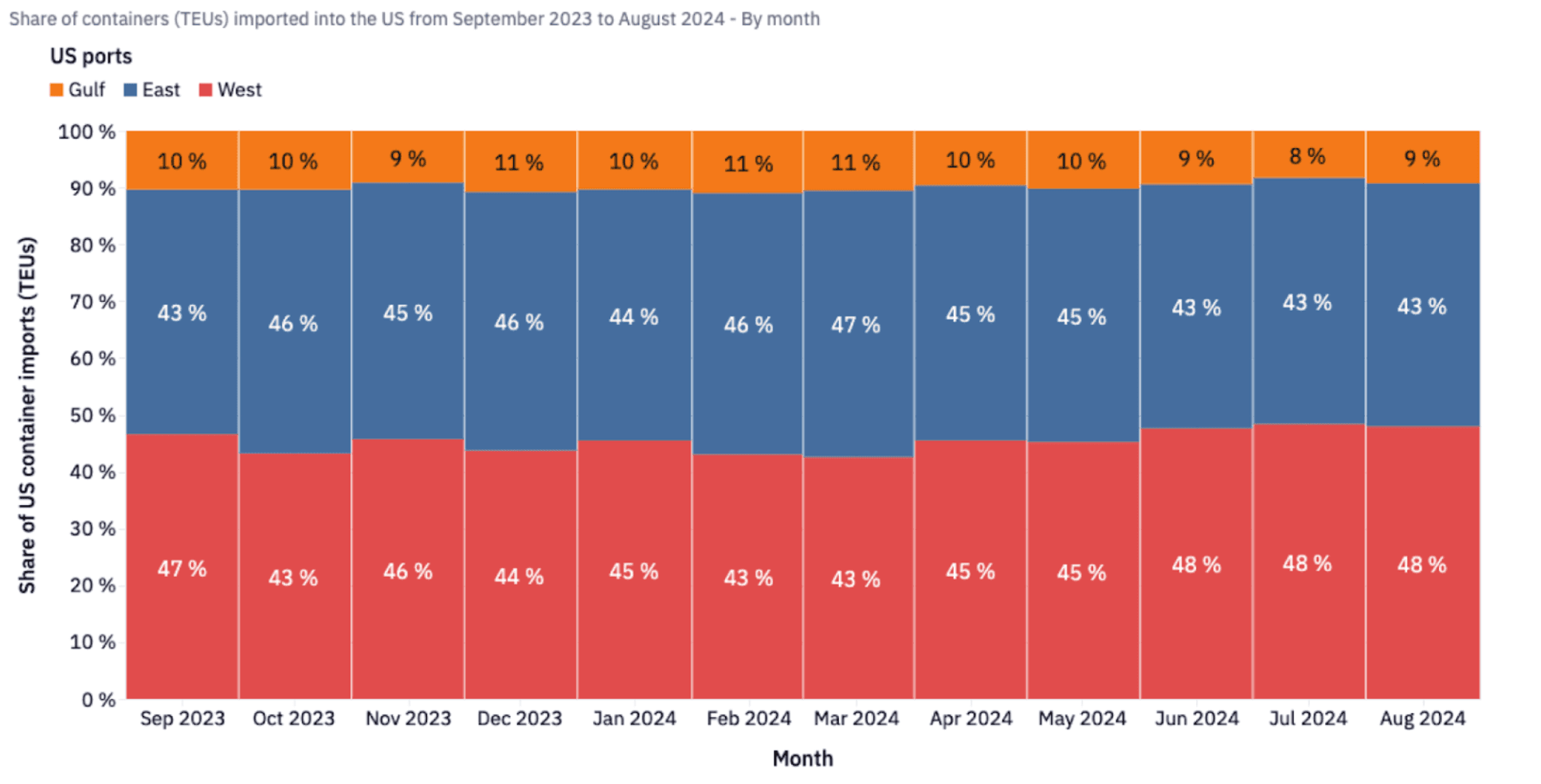
This strike is the first of its kind since 1977 in the region, and it being positioned so close to the peak shipping season made matters worse. Shippers, having learnt their lesson from several disruptions prior to the ILA showdown, started migrating their freight to the US West Coast over the last few months, which can be seen clearly from the graph below. While the US West Coast accounted for 43% of the total share of import TEUs in March, it grow to 48% by August.
Immediate Effect of The ILA Strike on Terminal Operators
The terminal operators are usually the first to feel the impact whenever a port strike happens because much of the operations rely on substantial labor. In this case, with over 45,000 workers striking, terminal operations shut down completely during this interval. These were the consequences that followed:
1. Idle Equipment and Reduced Productivity
The longshoremen are responsible for operating and maintaining equipment such as cranes, trucks, and other terminal equipment to run operations. Without them, the equipment would be idled. Considering the amount of capital spent procuring them, the terminal operators face mounting costs because they continue to pay for them while they idle without generating revenue.
2. Congestion and Space Constraints
While the strike was in place, the vessels could not successfully load or unload cargo. This resulted in a queuing of vessels all along the US East and Gulf Coast, with over 50 vessels on anchor, aside from the pile-up of containers at the terminal yards. As the ports spring back to action, these backlogs would take a while to be cleared, resulting in lower throughput and reduced operational efficiency.
3. Increased Demurrage and Detention Charges
Cargo owners and shippers may have to face the financial implications of the strike as it could pile up demurrage and detention fees. Considering a backup in terminal yards, finding an appointment for drayage carriers to move out containers can be challenging, with shippers often exceeding their last free day (LFD) and needing to pay demurrage over it. Such situations can create tension and strained relationships between the operators and shippers, impacting the working environment.
Delays and Disruptions For Shipping Companies
With no real way of unloading or offloading cargo to the ports, carriers or shipping companies were left stranded. Several ships anchored off the coast, while the rest were blanking sails or diverted to a different region. This led to:
1. Longer Transit Times
Shipping lines would have to hold the goods for longer than they like because they either have to anchor off the ports until they open or they must find alternative routes, both of which will have the same result of longer transit times.
2. Higher Operational Cost
Shipping lines incur additional costs from these delays and longer transits, whether rerouting or waiting at sea for the strike to be called off. This led them to charge extra fees in terms of emergency port charges (EPCs) and destination port charges (DPCs). Inevitably, this results in shippers paying extra for their freight that is destined for the East Coast or Gulf Coast ports.
3. Potential for Missed Schedules
If the ILA strike had continued longer, shipping schedules would have been in deep disarray as vessels would have been forced to miss windows and deadlines, which would have had a domino effect on downstream port of calls. In the long run, this would have caused an issue with finding empties, for them to be repositioned on time in export regions like China and SE Asia. Eventually, this would have caused a capacity crunch that would have spiked freight rates to the tune of what transpired in 2021.
The Ripple Effect on Freight Forwarders and Shippers
Depending on which expert you talk to, freight forwarders and shippers also bear the brunt of the impact of the ILA strike. They are currently grappling with delays, poor access to relevant data, increased costs, and customer dissatisfaction, which in a very competitive economy may have ripple effects on their business for months to come.
1. Supply Chain Delays
The 3-day ILA strike will make supply chains struggle to move goods effectively for close to a month. This is due to ports being choked with excess TEUs at their gates, paralyzing the efficiency of the terminals and yards. Business and supply chains that rely on imports moving via the US East and Gulf Coast are vulnerable to disruptions through October.
2. Rising Costs
Shippers might need to contend with higher freight rates. With a chunk of the cargo bought with capital on credit, the delay in turning over inventory would impact the bottom line as interest on that capital occurs. The financial burden may be devastating for the businesses involved, especially a high-volume, low-margin business like retail.
3. Strained Customer Relationships
With delivery deadlines pushed back and uncertainty surrounding shipments, customer relationships may be strained. Businesses that cannot meet their commitments risk damaging their reputation and losing long-term clients.
Navigating Shipping Turbulence With Terminal49
At Terminal49, we’ve always focused on making the unpredictable manageable for our customers. When the pandemic upended supply chains, companies turned to us for real-time container visibility—and that need hasn’t changed. Today, disruptions like the ILA strike and issues in the Red Sea highlight the importance of having the right data at the right time.
Our platform not only tracks containers but helps you navigate disruptions, whether it’s rerouted vessels, port closures, or backlogged ships. During the ILA strike, we launched a custom Containers Dashboard that allowed customers to track containers impacted by the disruption. The response was clear: 20% of users interacted with the feature, and 10% watched this tutorial on creating custom views, demonstrating the value of proactive risk management.
Disruptions are inevitable, but with Terminal49’s real-time visibility, terminal updates, and exception alerts, you can stay ahead. Our platform integrates seamlessly into your workflows, streamlining operations and minimizing delays. As peak season continues, visibility is essential. Connect with us today to stay prepared for what’s next.